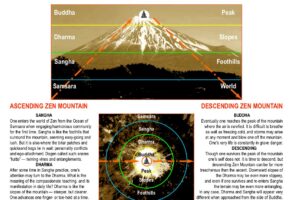
The Most Important Thing
It’s not obvious
though it’s in front of your face —
trust Dogen on this
DOGEN ON ZAZEN
Upon returning to Japan from China in 1227, at the age of 27, Master Dogen composed the first draft of Fukanzazengi, the tract in which he outlines the principles of seated meditation, or zazen, that he had learned under the tutelage of Master Rujing. In one of the English translations, about two-thirds of the way through the text, he asks a question of the reader:
Now that you know the most important thing in Buddhism, how can you be satisfied with the transient world? Our bodies are like dew on the grass and our lives like a flash of lightning, vanishing in a moment.
At this point in the piece, he has said many things about the physical method of meditation, interwoven with suggestions of the philosophy, attitude adjustments and correctives to conventional wisdom that accompany the practice. So what he means to indicate as the most important thing is subject to speculation. This may reflect a translator’s choice anomaly, a known issue in the art of interpreting ancient teachings.
To hone in on this most important thing more closely, let’s look at a brief, pointed poem, “Zazenshin,” that Dogen paraphrased from a Chinese version. It means something like “Acupuncture Needle” or “Lancet” – a very sharp instrument – for or about zazen:
Zazen-shin – Shohaku Okumura, trans.
The essential-function of each buddha
and the functioning-essence of each ancestor.
Being actualized within not-thinking.
Being manifested within non-interacting.
Being actualized within not-thinking, the actualization is by nature intimate.
Being manifested within non-interacting,
the manifestation is itself verification.
The actualization that is by nature intimate never has defilement.
The manifestation that is by nature verification
never has distinction between Absolute and Relative.
The intimacy without defilement is dropping off without relying on anything.
The verification beyond distinction between Absolute and Relative
is making effort without aiming at it.
The water is clear to the earth; a fish is swimming like a fish.
The sky is vast, extending to the heavens; a bird is flying like a bird.
So from this we may take it that the most important thing has something to do with not thinking and non-interacting, and not distinguishing between the absolute and relative. It is pointing at something intimate, undefiled by conventional wisdom, and that has nothing to do with our reliance on common understanding, and goal-oriented efforts. To which we can only respond, “Hmmm. Thank you Dogen, for clearing that up.”
MATSUOKA ON DOGEN
Clearly, this message is about something beyond words, that language can only point at, if it is beyond thinking itself. Let’s explore some more contemporary quotes from Matsuoka-roshi to see if we can zoom in on the meaning of these passages. O-Sensei simplified Dogen Zenji’s instructions for his American students, condensing them into three discrete areas: posture, breath, and attention. The following are three expressions he would use frequently, addressing questions about zazen:
Keep aiming at the perfect posture never imagining that you’ve achieved it
You have to work your way through every bone in your body
When your posture is approaching the stage of perfection,
it will feel as if you are shoving your head against the ceiling
The first, about aiming without achieving, makes Dogen’s “making effort without aiming at it” a bit more concrete by narrowly defining “it” as the upright posture. This is in keeping with the Zen premise that the zazen posture is the full expression of enlightenment, not merely a means to the end of enlightenment. It also reminds us that there can be no separation of body and mind in Zen, nor, indeed, in reality. And that the natural process of Zen is open-ended, based on aspiration as opposed to expectation.
The second indicates that this is going to be a steady, slow process on a visceral level, sitting “with muscle and bone,” as my senior dharma brother in Chicago, Kongo-roshi, titled one of his talks. There are a lot of bones in your body. And the bones, of course, are not separate from the skin, flesh, and marrow, the connective tissue, as Master Bodhidharma taught. “Working your way through” recalls the famous dictum from the poet Robert Frost, paraphrasing, “the only way out is through.”
The third seems to contradict the first, when Sensei describes what he frequently referred to as the “sitting-mountain feeling” that eventually comes from zazen. We are to aim at it without concluding that we’ve achieved it, because “Zen goes deeper,” as he would often say. No matter how seemingly complete and transcendent our immediate experience, it is not the end of the process, an attitude adjustment first articulated by Buddha himself in the “Fifty False States” section of the Surangama Sutra. The main admonition is that, no matter what happens in your meditation, not to imagine that you are now completely enlightened. Even Buddha returned to meditation for the fifty years of his life following his profound insight.
But this “shoving your head against the ceiling” sensation is something that I can personally attest to from my modest experience on the cushion. I suspect that when we pull back on the chin, stretching the back of our neck with strength, a specific detail of the posture emphasized by Matsuoka-roshi, it has the effect of shoving our skull against the scalp, which would then feel like the resistance of a solid, external surface like a ceiling. The entire body is a tension-compression structure, much like a camping tent, where the bones of the skeleton are the compression members under stress from the surrounding membrane of musculature, tendons and ligaments, like the canvas and ropes of the tent.
HAKUIN’S GAS PEDAL
The other end of the “tentpole” is the base of the spine, connecting to the coccyx, or tailbone. Hakuin Zenji, a famous Rinzai priest whose life span bridged the 17th and 18th centuries, from 1686 to1769, recommended that we push forward and down on the lower spine until we feel a bit of pain there. That sensation derives from stretching the hard tissue of the discs between the large lower vertebrae. Even more today than in his time, our posture tends to be c-shaped, sometimes referred to as a “cashew,” when we sit in the driver’s seat of our vehicles on the expressway, or the chair at our desk. The natural position of the spine is an “S-shape” curve, bending the lower back in the opposite direction, like a cobra rising from the floor, dancing to the tune of the snake-charmer’s flute.
I call this Hakuin’s gas pedal. Like the accelerator of your car or truck, if you keep your foot on it, pressing forward and down, the vehicle moves. If you let up on it, it slows to a stop. On the other hand, if you go pedal to the metal, it speeds out of control. The Middle Way again, in all its manifestations.
So the most important thing, as regards the posture, at least, may be keeping these two pressure points in play while sitting. If you do so, you can’t go far wrong in terms of sitting upright. Breathing and attention also come into the picture, but that may be a subject for another UnMind. Let me close this segment with a couple of aphorisms that have come to me in my practice.
ME ON ZAZEN
I do not claim to have the depth of insight and understanding of our ancestors, and recognize that context, while not determinative of Zen experience, certainly counts. What Buddha, Bodhidharma, the great ancestors in China, and Dogen himself managed to accomplish under relatively primitive conditions in no way compares to what we may expect to realize under relatively cushy but geometrically more complex circumstances. But as they did in their times we must do in ours — namely use what we know to inform our efforts in exploring what we do not know, and cannot know, in any ordinary sense. So, here, I want to introduce two terms that may have no counterpart in their language.
PROPRIOCEPTION MEETS VERTIGO
Proprioception is a term from modern physiology, defined as:
Perception or awareness of the position and movement of the body
Vertigo is defined as:
A sensation of whirling and loss of balance, associated particularly with looking down from a great height, or caused by disease affecting the inner ear or the vestibular nerve; giddiness.
In terms of our experience in zazen, then, proprioception would be akin to samadhi, or at least its early stages, when, as Matsuoka-roshi said:
When posture, breath, and attention all come together in a unified way, that is the real zazen.
Now, if there is “real” zazen, it implies that there must be “unreal” or “fake” zazen, or the false impression that we are doing zazen when we are not, really. Samadhi is a jargon term that I hesitate to use, as it implies that I know what it means while suggesting that you probably do not. Which sets up the false dichotomy of “you and I,” “us and them,” the in-group cognoscenti versus the great unwashed. Sensei also pointed out, at the Zen Buddhist Temple of Chicago, paraphrasing, “When you become dizzy, concentrate on your knees.” And “When you get nauseous, concentrate on your forehead.” Or it may have been the other way around. The main point is that you probably will get dizzy, and you probably will get nauseous, in zazen.
This brings up another coinage, for which I claim authorship:
Let not the spiritual be the enemy of the practical
I detect a vestigial strain of puritanism in the American culture that can infect our understanding and presentation of Zen, as a kind of belief system, a set of doctrines that one must subscribe to, in order to penetrate the inner sanctum of Zen’s purported spiritual secrets. This is anathema to the real Zen, as I understand it.
All of Master Dogen’s instructions in Fukanzazengi are physical, not mental, as Carl Bielefeldt points out in his “Dogen’s Manuals of Zen Meditation,” a wonderful, incisive line-by-line analysis of Dogen’s two extant revisions compared to the Chinese original. So let’s stay focused on the physical, and not get distracted by any woo-woo “spiritual.”
If we continue sitting without expectation, implementing the two pressure points until we feel tMatsuoka-roshi’s “sitting mountain feeling” of great stability — our head “pressed against the ceiling” — the body and mind will take us where we need to go. We trust our teachers’ intent and wisdom, and we trust our Original Mind, as indicated in the title of Hsinhsinming, the earliest Ch’an poem chanted in Soto liturgy.
If we sustain this posture — sitting still enough and straight enough for long enough — it will work its magic. Equilibrium will set in in the tension-compression system of muscle and bone of the body, leading to equipoise of the mind. Sustained for some time, the constancy of our proprioception will inevitably lead to vertigo — the flip side of solidity. “Mountains are always walking” — the planet is falling through space. There is “not even a toehold.” Emptiness is innately form, form innately emptiness.